
The intended audience for this document are software architects, designers and developers aiming to implement an integration between their system/solution and the Global Payments Marketplace.
Markets and endpoint locations
Global Payments Marketplace (GPM) is operated as a multi-market solution, where each market is supported with a separate set of endpoints. Endpoint locations that correspond to markets are:
| Market | Base endpoint | SSO/IdP realm | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
Czech Republic |
mygp-cz |
live |
|
Slovakia |
mygp-sk |
live |
|
Austria |
mygp-at |
live |
|
Romania |
mygp-ro |
live |
Following purpose-specific endpoint locations are supported besides the market-bound endpoint locations listed above:
| Market | Base endpoint | SSO/IdP realm | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
Global |
mygp-global |
live |
Locales
Due to multi-market deployment, GMP supports multiple locales (languages and formatting conventions):
| Locale | Status |
|---|---|
cs-CZ |
live |
sk-SK |
live |
en-US |
live |
de-AT |
live |
ro-RO |
live |
Environments
Once an endpoint location is live, it supports following types of environments:
-
Live environment is running production workloads and is connected with real users and customer data. Access to live environment is granted to systems and applications that have passed through the QA and verification process.
-
Uat2 environment is a staging environments for workloads that are being subject to QA and verification process before deployment to production. It normally runs the same version of Marketplace system as production, except during the deployment transition window when it receives a version designated for deployment to production.
-
Uat1 environment is an integration environment provided to facilitate development and integration of partner solutions. It normally runs a version of Marketplace system that is ahead of production.
URL conventions for environments
URLs provided across all endpoint locations follow a common convention that is based on combination of base endpoint and the type of the environment.
Environment/location specific URL for the marketplace portal is defined as:
-
<base endpoint> for live environment
-
uat2.<base endpoint> for UAT2 environment
-
uat1.<base endpoint> for UAT1 environment
Example: marketplace portal in UAT1 environment for Czech Republic is accessible at https://uat1.mygp.cz
Single sign-on for users
This section discusses the single sign-on (SSO) integration between a partner web site and GP marketplace SSO, where partner web site is taking the role of relying party and Global Payments Marketplace (GPM) SSO is acting as the identity provider. It provides an overview and information about following SSO integration scenarios and use cases:
-
Generic user authentication with OpenID Connect (OIDC)
-
User authentication with home-realm discovery
-
Simple user authentication scenario with browser redirect initiated from marketplace
Integration with single sign-on can be used for authentication of end users (GP customers or people working for GP customers) and internal users (e.g. telesales or sales support agents). OpenID Connect is used as the principal integration protocol for authentication of user access to GPM and connected 3rd party applications.
GPM is a multi-market solution where each market is using a dedicated SSO realm that handles specific market localisation (mainly language). Whenever the relying party requires an access token that is issued for specific user identity it must first initiate home-realm discovery request to receive back the destination URL for the SSO authentication request (through the auth_url property).
Generic user authentication with OpenID Connect
This use case is relevant for relying parties (applications or systems seeking to authenticate users through GPM SSO) that do not need to authenticate users in the context of their business contracts with GP. This means that identity of the user is important, but company/contract information is not relevant. E.g. when relying party wants to authenticate internal users.
Detailed specification of authorisation code flow is available in the OpenID Connect documentation.
Prerequisites for integration
Before the 3rd party partner can start using OIDC authentication function, the partner must be in possession of a marketplace partner account and a 3rd party application must be registered with the partner account.
The 3rd party application can then be approved and configured for OIDC authentication with following parameters:
-
list of valid OIDC redirect (callback) URLs.
-
base URL of application (where users can be redirected back in case of failed authentication attempt)
Once this configuration is completed, the home-realm-discovery function is activated for the application and partner is issued with SSO generated client id and client secret parameters that are required to perform OIDC authentication operations.
In order to complete SSO integration, the 3rd party application must implement features described in the next sections.
Authentication request
Authentication request is performed as a HTTP GET redirect request from the 3rd party web site to the OIDC authorisation request endpoint of the SSO. The redirect is performed with assistance of the user agent (normally a web browser).
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Location: https://mygp.global/auth/realms/mygp-global/protocol/openid-connect/auth?
response_type=code
&scope=openid
&client_id=example-client-id
&state=af0ifjsldkj
&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fclient.example.org%2Fcb
Authorisation code callback
Authorisation code callback is performed as a HTTP GET redirect request from the SSO web site back to the 3rd party web site. The redirect performed with assistance of the user agent (normally a web browser) and carries information that is relevant for the verification of submitted data as well as conversion of authorisation code into ID or access token.
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Location: https://client.example.org/cb?
code=SplxlOBeZQQYbYS6WxSbIA
&state=af0ifjsldkj
Authorisation code conversion
Authorisation code conversion is performed as a back-channel HTTP POST request issed from 3rd party web site towards the SSO token endpoint URL. This is a direct HTTP request from 3rd party back-end to the SSO token endpoint.
POST /auth/realms/mygp-global/protocol/openid-connect/token HTTP/1.1 Host: mygp.global Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Authorization: Basic example-client-secret grant_type=authorization_code &code=SplxlOBeZQQYbYS6WxSbIA &redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fclient.example.org%2Fcb
Response returned by the SSO token endpoint will carry a JSON object with requestd ID or access token.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Cache-Control: no-store
Pragma: no-cache
{
"id_token": "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IjFlOWdkazcifQ.ewogImlzc
yI6ICJodHRwOi8vc2VydmVyLmV4YW1wbGUuY29tIiwKICJzdWIiOiAiMjQ4Mjg5
NzYxMDAxIiwKICJhdWQiOiAiczZCaGRSa3F0MyIsCiAibm9uY2UiOiAibi0wUzZ
fV3pBMk1qIiwKICJleHAiOiAxMzExMjgxOTcwLAogImlhdCI6IDEzMTEyODA5Nz
AKfQ.ggW8hZ1EuVLuxNuuIJKX_V8a_OMXzR0EHR9R6jgdqrOOF4daGU96Sr_P6q
Jp6IcmD3HP99Obi1PRs-cwh3LO-p146waJ8IhehcwL7F09JdijmBqkvPeB2T9CJ
NqeGpe-gccMg4vfKjkM8FcGvnzZUN4_KSP0aAp1tOJ1zZwgjxqGByKHiOtX7Tpd
QyHE5lcMiKPXfEIQILVq0pc_E2DzL7emopWoaoZTF_m0_N0YzFC6g6EJbOEoRoS
K5hoDalrcvRYLSrQAZZKflyuVCyixEoV9GfNQC3_osjzw2PAithfubEEBLuVVk4
XUVrWOLrLl0nx7RkKU8NXNHq-rvKMzqg"
"access_token": "SlAV32hkKG",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 3600,
}
User authentication with home-realm discovery
Home-realm discovery is a means to discover (at runtime) appropriate endpoints and parameters to initiate OIDC authentication as well as qualify the business context of the authentication, such as the business ID (e.g. IČO) for the company the user is authenticating for. This use case is relevant for authentication of end users (GP customers or people working for GP customers), where the relying party requires information about exact company/contract the end user has selected for authentication.
While the need for more narrow qualification of the business context will vary from one SSO client use case to another the general need for this qualification can be understood from the following data model:

An individual SSO user account can be related - indirectly via the Person entity - to more than one contract and company and for some (even most) use cases it is important for the relying party (SSO client) to know the exact contract (or company) that the user is performing the authentication for.
The purpose of home-realm discovery function is to perform business context qualification in advance of OIDC authentication to the relying 3rd party system or application. The scope of qualification includes:
-
market (CZ, SK, etc),
-
business_id or company_key.
Provisioning and activation
Before the 3rd party partner can start using the home-realm discovery function, the partner must be in possession od a marketplace partner account and a 3rd party application must be registered with the partner account.
The 3rd party application can then be approved and configured for home-realm discovery with following parameters:
-
market mapping policy (none or required),
-
company mapping policy (none, business_id or company_key),
-
alternative user name mapping policy (none or omsuid),
-
home-realm-discovery callback URL (exact URL),
-
secret key (used to encrypt and decrypt response data),
-
list of valid OIDC redirect (callback) URLs.
Once this configuration is completed the home-realm-discovery function is activated for the application and partner is issued with SSO generated client id and client secret parameters that are required to perform OIDC authentication operations.
Home-realm discovery request
A home-realm discovery request is initiated by the 3rd party application with a HTTP GET redirect request that must be executed through the user agent (such as web browser).
The redirect URL must be formatted as:
-
https://uat1.mygp.global/discovery?state={?state}&cauth={?cauth} for development system
-
https://uat2.mygp.global/discovery?state={?state}&cauth={?cauth} for pre-production system
-
https://mygp.global/discovery?state={?state}&cauth={?cauth} for live system
Query string parameters:
-
state is an arbitrary string produced by the 3rd pary app that is used to uniqely identify the request (i.e. prevent browser or an intermediary proxy to return cached response) as well as to link the request with the response received later through the callback. Maximum allowed length is 64 characters.
-
cauth must contain the application key ID that was assigned to the 3rd party app; this ID is used by the server to identify the 3rd party app and associated configuration parameters (including shared key). The parameter is generated as a random string (e.g.
xYDEb7SjeGlGhx0w) that is safe to be passed in the URL.
state = 'bcd6da3ab4a814ddf8798fed4e12cf02bcdca838fe92127bb4c03899a7bb2210' cauth = 'xYDEb7SjeGlGhx0w' # Resulting home realm request URL https://mygp.global/discovery?state=bcd6da3ab4a814ddf8798fed4e12cf02bcdca838fe92127bb4c03899a7bb2210&cauth=xYDEb7SjeGlGhx0w
Home-realm discovery callback
3rd party application must implement a home-realm discovery callback endpoint where the marketplace SSO will redirect user agent when the discovery and business context qualification process is completed. The redirect is executed as as a HTTP form POST request (executed by the user agent - web browser - on behalf of the authenticating user) and the request body contains transactional parameters that the 3rd party app can use to decrypt the response.
POST /app/specific/callback/path?state={?state} HTTP/1.1
Host: www.relying-party.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 581
x-cbc-iv=c89899de29096e31f993974bf608fd40&x-claims=uR6T5zovuWglcse70cNEUwFZHrt%2BJVfmakqXFvGJQ4%2FK%2BhuLxlzWCIqk1euBXU6jk9wNFJRteOG1RPHcc0WTaO5JMGvYWmepjjBnIOwB2lORWGj4ORs9bwpT3cv0Mmm1HjOqsEvpMYORWOD8tZUqNW7gzhi8Z8sAAmleeJ8GRQh4MQAbBWv%2B1B0UV0RXT7p%2Bn5XEirTceYw4NPJTWHE8e4dCKoJjpqOwIq375Tb2rfC6zGgoBRYllgEWIOcH7b3QNHjW2GGX8WhPfCiGqR9CLIxv2tAo2hDoypPtDvWq5rYgecPL6szjbq23SAWHiP5NxlKlDA0dWg1pwel3N4uRAV%2Bk5dG1Ru2%2BgXQQTg12n0k4JzuRH1nOwV0NoqNJ7ALg8dfN%2FT2psxpf%2BAEhaeGV9heRNFmXc5TWKlwIl1BNbNqxjoiWdlIDTIcpiWYaEF3t8Co7g%2B6GhMWLtzzrAAkS4RsKGKLLrduIGMfHDpBjuTDdAOzHa%2FjZ%2Fw3PEUUQBrnO
Query string parameters:
-
state is set to the value provided by the 3rd party application with the initial home-realm discovert request. 3rd party app must perform a correlation validation for the value and reject any requests that do not pass this validation.
Request body parameters:
-
x-cbc-iv contains the value for initialisation vector, which is represented as a 32-characters hexadecimal string. The value
c89899de29096e31f993974bf608fd40corresponds to the byte array [c8, 98, 99, …, fd, 40]. -
x-claims contains encrypted JSON object with claims. The value of the field is base64 encoded and encrypted with AES-256 CSB algorithm.
Structure of JSON claims object:
{
'state': '{?state}',
'business_id': '098765432112',
'company_key': '23b1d7bcdb6fc513ba0edd8957943b6c30425948',
'sso_subid': '19260239-2340-43ef-b49b-ad585b39eb07',
'sso_username': 'mpuser1',
'alt_username': 'sp67347384',
'given_name': 'User 1',
'family_name': 'MPL',
'market': 'cz',
'auth_url': 'https://sso.mygp.cz/auth/realms/mygp-cz'
}
-
state must match the value of state parameter provided in the query string
-
business_id (IČO)
-
company_key
-
sso_subid is the unique and permanent ID assigned by the SSO to the user account
-
sso_username username that was used for authentication to SSO
-
alt_username alternative application specific username
-
given_name
-
family_name
-
market two letter code of the country/market
-
auth_url used for SSO authentication request
Encryption algorithm and management of secrets
The data submitted with the home-realm discovery callback will be encrypted using AES-256 algorithm using CBC block mode with PKCS#7 padding. The content (JSON text) will be converted to UTF-8 prior to encryption.
The value for IV, which will be initialised with random data for each request, will be provided to the relying party
though the x-csb-iv field in the HTTP POST request body.
The encryption key will be unique and specific to the cauth. Both cauth and encryption key will be generated when the app account will be registered in the system and will be provided to the partner in a password-protected ZIP file. Both secrets can be rotated independently of one another (e.g. encryption key can be rotated without changing cauth and vice versa).
Example:
# 16-byte IV
IV = "732b7cfbeaf99313"
# 32-byte / 256-bit key
key = "c5ce45f758a361a24d43079fdcefbf5b"
# JSON data serialized to string
input = "{\n 'state': '{?state}',\n 'business_id': '098765432112',\n 'company_key': '23b1d7bcdb6fc513ba0edd8957943b6c30425948',\n 'sso_subid': '19260239-2340-43ef-b49b-ad585b39eb07',\n 'sso_username': 'mpuser1',\n 'alt_username': 'sp67347384',\n 'given_name': 'User 1',\n 'family_name': 'MPL',\n 'market': 'cz',\n 'auth_url': 'https://sso.mygp.cz/auth/realms/mygp-cz'\n}"
# Base64 encoded encrypted output
b64_output = "tNDhDA8NLjDF1nNULNJe6gVlXABzJ3ScqoZWBpPbcQL/BuFqLfJiJCH2+DFyWf9RykOsAei8v/+5NBAxF0J10NHYRiV6yvlm8L3xK6qKtrGPgnfqritEjVjlJUK/mlzb8fZIDXMoWeVZbZ9PCdV+BiHXUeWUt3cQ0ARHfAKkcsbJls7iR9i6WCc7MaiYrT533Kq24XLI01LH24dpAUIC/JyN81iArjykB6DZkuxNCoXPrMgYeVL2uHG4iIrtj30yl+Ob7MyCAXuth+/+ldDcyX57EfAJlvfcwyAIQpxsnD61HsemyVuWAQ7iz9EGrNHt02l/xZYQI0LweADA6X+HEJKZWVl4cIc0+vWRA2LFd0ybTe0cy3djRmyk4h+n5b0QEnjeMjb1sWtf2Yxqhbs3iesLLgQtvj+R5t+SoskaS7Dto8ny5i/oc9NGhLoeBjRPAtPAafDTM69x9WP7dlZmOqPgssE05rSQQ2UUTrB/HNDZK/8JRHvUbz7vbJi1/ubR"
External references:
Rotation of secrets
Relying application can have fore than one pair of secrets (key_id and secret_key) active at the same time and
can (freely) choose which secret will/should be used for the request. The selection of the key is communicated
with the cauth (mandatory) parameter in the initial home-realm discovery request.
Rotation of the secrets can be performed with the following steps:
-
Application is configured to use
current-secretpair. All discovery requests are initiated and performed with this secret pair. -
New secret pair -
new-secret- is created on the marketplace for the application. This does not have impact on incoming discovery requests. -
New secret pair is configured in the application. All discovery requests initiated after that change are performed with the new secret pair.
-
After a period of time, the old
current-secretwill be deactivated on the marketplace and any requests submitted with thatcauthkey id will be rejected.
Important to note is that home realm discovery request started before step #3 will be performed using the
current-secret pair. It is therefore possible that callback requests will arrive after #3 that will carry request
body encrypted with the old secret. Application logic should be able to successfully process such callback
requests.
Simple authentication scenario (login initiated from 3rd party site)
This scenario is applicable for 3rd party applications that use marketplace SSO strictly for the purpose of user identification and DO NOT call any marketplace APIs on behalf of the user.

Once the processing of the HTTP POST request submitted to the callback endpoint is completed successfully, the identity of the user should be treated as verified and valid and authenticated application session can be started for the user.
Simple authentication scenario (redirect initiated from marketplace)
Partner web sites that integrate with GPM SSO must implement a dedicated landing page, which will be used on the marketplace portal to redirect users to the partner web site. For 3rd party web sites that employ the "simple authentication scenario" the behavior of this landing page must be almost identical to the behavior of the home-realm discovery callback endpoint with the exception of state parameter that - in this scenario - will not be set.
POST /app/specific/landing-page/path HTTP/1.1 Host: www.relying-party.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Content-Length: 581 x-cauth=xYDEb7SjeGlGhx0w&x-cbc-iv=c89899de29096e31f993974bf608fd40&x-claims=uR6T5zovuWglcse70cNEUwFZHrt%2BJVfmakqXFvGJQ4%2FK%2BhuLxlzWCIqk1euBXU6jk9wNFJRteOG1RPHcc0WTaO5JMGvYWmepjjBnIOwB2lORWGj4ORs9bwpT3cv0Mmm1HjOqsEvpMYORWOD8tZUqNW7gzhi8Z8sAAmleeJ8GRQh4MQAbBWv%2B1B0UV0RXT7p%2Bn5XEirTceYw4NPJTWHE8e4dCKoJjpqOwIq375Tb2rfC6zGgoBRYllgEWIOcH7b3QNHjW2GGX8WhPfCiGqR9CLIxv2tAo2hDoypPtDvWq5rYgecPL6szjbq23SAWHiP5NxlKlDA0dWg1pwel3N4uRAV%2Bk5dG1Ru2%2BgXQQTg12n0k4JzuRH1nOwV0NoqNJ7ALg8dfN%2FT2psxpf%2BAEhaeGV9heRNFmXc5TWKlwIl1BNbNqxjoiWdlIDTIcpiWYaEF3t8Co7g%2B6GhMWLtzzrAAkS4RsKGKLLrduIGMfHDpBjuTDdAOzHa%2FjZ%2Fw3PEUUQBrnO
Request body structure (with decrypted example):
{
'business_id': '098765432112',
'company_key': '23b1d7bcdb6fc513ba0edd8957943b6c30425948',
'sso_subid': '19260239-2340-43ef-b49b-ad585b39eb07',
'sso_username': 'mpuser1',
'alt_username': 'sp67347384',
'given_name': 'User 1',
'family_name': 'MPL',
'market': 'cz',
'auth_url': 'https://sso.mygp.cz/auth/realms/mygp-cz'
}
Submitted data will be encrypted using the encryption key indicated with the `x-cauth parameter. If the application
will maintain multiple active secrets, then the oldest active secret will be used for encryption.
Custom claims
The claims set prepared by the home realm discovery component can include custom claims that can be used by the receiving application to modify and improve customer experience.
| Name | Domain | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
channel |
string |
mygp.cz |
Identifies domain name for the submitting channel (portal). |
language |
string |
cz |
Identifies preferred language (of the user). |
Registration and pairing of user accounts
Customer data is not automatically paired with user accounts. This linking in performed through user account
registration and pairing process. The process is initiated by opening a unique URL link that is (normally)
provided to users through e-mail and may take the form similar to https://uat1.mygp.cz/onboarding/QwZN0_clk4ItotzKS1UQCsIHsh8zugoy.




Marketplace APIs
Request endpoints
URL schema for marketplace APIs is extending the baseline schema described in section "Markets and endpoint locations". Root URL for marketplace API resources is derived from base endpoint as https://{env-prefix}-api.{base-domain}.
Example: root URL of marketplace API resources in Uat1 environment for market in Czech Republic is https://uat1-api.mygp.cz.
Versioning
URL schema is further extended with API version information. Clients must explicitly select desired API
version by starting the API request path with /v{N} prefix.
Example: URL for API v1 example resources in Uat1 environment for market in Czech Republic is https://uat1-api.mygp.cz/v1/examples.
Request correlation
Request and response correlation between GPM and 3rd party system (regardless of which side is submitting the
request) is carried via the RequestID HTTP header. Initiating party is expected to generate a random UUID for
the request ID and passing it to the receiving party with the RequestID` HTTP request header.
The receiving party is expected to replay the value in the HTTP response header returned to the initiating party.
The purpose of the RequestID header is to facilitate location of relevant information (log records) in the
process of troubleshooting issues across both systems.
Request authentication
All Marketplace APIs use a bearer token authentication scheme supported by OIDC issued JWTs for authentication and authorization of requests. Depending on the type of resource and operation the clients are required to provide an appropriate access token with each request:
-
Service account access token identifies the system issuing the request. Such access tokens are typically obtained using the client credentials grant.
-
User account access token identifies the user who initiated the action that resulted in the API request. Such access tokens are typically obtained using the authorization code (web) flow and require user’s participation facilitated through a user agent (e.g. web browser, mobile application, etc).
OpenID Connect client credentials flow must be used by the initiating party to obtain an access token (JWT) and passed it in the Authorization header of the HTTP request.
A SSO client account is required to implement and operate API authentication. Client account is defined with following properties (also known as client credentials):
-
client id
-
client secret
Both properties are required for processing of OIDC transactions and must be treated as sensitive information. If any of these parameters become compromised, you are obliged to rotate the secrets. For this reason it is important to think about rotation of secrets when you design the integration solution.
Before making a request to the API endpoint, the requesting party (API client) must obtain an access token from the relevant identity provider service. Make note that every endpoint location provides a corresponding OIDC identity provider endpoints and that unless otherwise stated, the client must authenticate an API request with the access token issued by the identity provider service from the same endpoint location (e.g. API request sent to https://api.mygp.global must be authenticated with an access token issued by https://mygp.global identity provider service).
Obtaining access token with client credentials grant
This grant type is used for machine-to-machine authentication, where API requests are made under the identity of the requesting system rather than the (end-)user.
The grant type is executed as a single HTTP POST request to the OIDC token URL.
POST /auth/realms/mygp-global/protocol/openid-connect/token HTTP/1.1 Host: mygp.global Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=client_credentials &client_id=my-app-client-id &client_secret=ae58c8d1-0d8e-4a15-ac21-76164a3860d9
Access and refresh tokens (in JWT form) are returned in the response body.
{
"access_token":"eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCIgOiAiSliwia2l...k0Q_LshbwqYxIGNyg",
"expires_in": 900,
"refresh_expires_in":14400,
"refresh_token":"eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCIAiSld...oDbGUhirkNjVa1ImyK4z60-5HxZo",
"token_type":"bearer",
"not-before-policy":1535638531,
"session_state":"988af955-cc4c-44ba-99d8-43a8dbe5b581",
"scope":""
}
The various properties returned in the JSON object are:
-
token_type defines the type of token(s) returned in the request; it is expected to be bearer which makes it usable as an authentication credential when making API requests.
-
access_token contains a string value that represents a JWT encoded access token.
-
expires_in defines the time-to-live (TTL) period for the access token; the value represents the length of TTL period in seconds. Once the access token expires it can no longer be used for authenticating API requests and the client must obtain fresh access token. Access tokens are generally short-lived.
-
refresh_token contains a string value that represents a JWT encoded refresh token. Refresh token can be used by the client to obtain a fresh access token using the refresh token grant type (see bellow).
-
refresh_expires_in defines the TTL period for the refresh token in seconds. Once the refresh token expires it can no longer be used for obtaining fresh access tokens.
Obtaining access token with refresh token grant
If client is in possession of a valid refresh token, then it can use the refresh token grant requests to obtain fresh access tokens.
If client secret was used to obtain initial refresh token, then the client_secret parameter must also be included in the refresh token grant request!
POST /auth/realms/mygp-global/protocol/openid-connect/token HTTP/1.1 Host: mygp.global Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=refresh_token &client_id=my-app-client-id &client_secret=ae58c8d1-0d8e-4a15-ac21-76164a3860d9 &refresh_token=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCIAiSld...oDbGUhirkNjVa1ImyK4z60-5HxZo
The structure of the response body (JSON) is the same as for client credentials grant.
Frequency of access token retrieval
SSO OpenID Connect token endpoint has throttling policy applied that is designed to prevent (D)DoS attacks, meaning that client should carefully manage access tokens and reuse them while they are still valid.
Requesting new access tokens with high frequency may result in client receiving rate-limit rejections.
Passing access token with API request
Access tokens are passed in the Authorization HTTP request header when making API requests for protected resources. Header value must be composed of the token type (Bearer) and JWT string, which must be separated by a single space (ASCII code 32).
PUT /subscriptions/{subscription_id} HTTP/1.1
Host: api.mygp.global
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 581
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCIgOiAiSliwia2l...k0Q_LshbwqYxIGNyg
RequestId: 1CAC7410-744B-44F2-B02E-5C15710D3F0D
{
...
}
JWT token validation
Applications and systems that support the described bearer token authentication scheme must ensure that all tokens received through incoming HTTP requests are correctly validated to prevent malicious attackers to obtain access to sensitive data. Most available JWT libraries support this validation out-of-the-box. The validation checklist should include:
-
verification of signing algorithm (
alg) -
verification of JWT cryptographic signature
-
verification of issuer (
iss) -
verification of expiration time (
exp) -
verification of not before constraint (
nbf)
Keys required to (re-)calculate JWT cryptographic signature can be downloaded from the publicly available OIDC endpoints. The URL pattern for these URLs is <base-endpoint>/auth/realms/<location-realm>/protocol/openid-connect/certs, where base-endpoint and location-realm must be substituted according to market and environment.
Examples:
| Base endpoint | SSO/IdP realm | URL |
|---|---|---|
mygp-cz |
https://mygp.cz/auth/realms/mygp-cz/protocol/openid-connect/certs |
|
mygp-sk |
https://uat2.mygp.sk/auth/realms/mygp-sk/protocol/openid-connect/certs |
|
mygp-at |
https://uat1.mygp.at/auth/realms/mygp-at/protocol/openid-connect/certs |
Validation of JWT bearer tokens can also be delegated to a middleware functions at the application boundary. Most API management systems support validation of OIDC bearer tokens out of the box (e.g. https://tyk.io/docs/basic-config-and-security/security/your-apis/openid-connect/). Alternatively it is also possible to use client adapters provided by Keycloak.
For additional details and step-by-step guide consult "Validate JSON Web Tokens" article or Section 7.2. of the JWT RFC.
User profile information API
This chapter describes APIs available to partner systems to access extended information about users.
The API can replay with one of the following HTTP status codes:
-
200 - request is valid and the user profile was retrieved successfully
-
401 - authentication credentials (JWT token) were missing or could not be validated
-
403 - authentication credentials do not carry required authorisation
-
404 - request is valid but there is no business selected
GET /user-profiles/self HTTP/1.1
Host: mygp.global
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
{
"business_id": "7587485784",
"first_name": "Joe",
"last_name": "Grizzly",
"email": "joe.grizzly@example.org"
}
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 40x:
{
"code": "40x",
"message": "name of the error",
"description": "description details of the error",
}
Merchant information API
This chapter describes APIs available to partner systems to access information about merchants and the setup of acquiring services.
Companies
This API is used to retrieve representation/data for specific merchant company.
The API can replay with one of the following HTTP status codes:
-
200 - request is valid and the company was retrieved successfully
-
401 - authentication credentials (JWT token) were missing or could not be validated
-
403 - authentication credentials do not carry required authorisation
-
404 - request is valid but the company was not found for the requested business ID
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 20x:
GET /companies/{business_id} HTTP/1.1
Host: mygp.global
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
{
"business_id": "7587485784",
"company_name": "Global Payments s.r.o.",
"registered_address": {
"street": "V Olšinách",
"house": "626/80",
"city": "Praha",
"zip_code": "10 100 00",
"country_code": "CZ"
},
"activated": "2018-05-12",
"updated": "2020-09-27T10:16:12"
}
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 40x:
{
"code": "40x",
"message": "name of the error",
"description": "description details of the error",
}
Company List
This API is used to retrieve list of active companies on market.
The API can replay with one of the following HTTP status codes:
-
200 - request is valid and the company list was retrieved successfully
-
401 - authentication credentials (JWT token) were missing or could not be validated
-
403 - authentication credentials do not carry required authorisation
-
404 - request is valid but there is no business selected
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 20x:
GET /companies HTTP/1.1
Host: mygp.global
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
{
"count": 2
"next": null,
"previous": null,
"results": [
{
"business_id" : "7587485784",
"company_name" : "Happy Koala Ltd.",
"activated" : "2019-07-01",
"updated" : "2019-07-01T01:00:00",
"self" : "https://mygp.global/v1/companies/7587485784"
},
{
"business_id" : "9387485321",
"company_name" : "Shark Koala Ltd.",
"activated" : "2019-07-01",
"updated" : "2019-07-01T01:00:00",
"self" : "https://mygp.global/v1/companies/9387485321"
}
]
}
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 40x:
{
"code": "40x",
"message": "name of the error",
"description": "description details of the error",
}
Locations
This API is used to retrieve representation/data for specific merchant location.
The API can replay with one of the following HTTP status codes:
-
200 - request is valid and the location was retrieved successfully
-
401 - authentication credentials (JWT token) were missing or could not be validated
-
403 - authentication credentials do not carry required authorisation
-
404 - request is valid but failed to retrieve data because:
-
location was not found for the requested MID
-
location was found but no company was found for that location
-
-
-
409 - request is valid but multiple locations were found for the requested MID
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 20x:
GET /locations/{mid} HTTP/1.1
Host: mygp.global
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
{
"mid": "88587548578",
"business_id": "7587485784",
"location_type": "outlet",
"location_name": "Main Street Shop",
"address": {
"street": "V Olšinách",
"house": "626/80",
"city": "Praha",
"zip_code": "10 100 00",
"country_code": "CZ"
},
"activated": "2018-05-12",
"updated": "2020-09-27T10:16:12"
}
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 40x:
{
"code": "40x",
"message": "name of the error",
"description": "description details of the error",
}
Location List
This API is used to retrieve list of locations for a specific company.
The API can replay with one of the following HTTP status codes:
-
200 - request is valid and the location list was retrieved successfully
-
401 - authentication credentials (JWT token) were missing or could not be validated
-
403 - authentication credentials do not carry required authorisation
-
404 - request is valid but the business ID was not found
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 20x:
GET /companies/{business_id}/locations HTTP/1.1
Host: mygp.global
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
{
"count": 2
"next": null,
"previous": null,
"results": [
{
"mid" : "7587485784",
"location_name" : "Main Street Shop",
"location_type" : "outlet",
"activated" : "2019-07-01",
"updated" : "2019-07-01T01:00:00",
"self" : "https://mygp.global/v1/locations/7587485784"
},
{
"mid" : "6357485222",
"location_name" : "www.mainstreetshop.com",
"location_type" : "ecommerce",
"activated" : "2019-07-01",
"updated" : "2019-07-01T01:00:00",
"self" : "https://mygp.global/v1/locations/6357485222"
}
]
}
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 40x:
{
"code": "40x",
"message": "name of the error",
"description": "description details of the error",
}
Terminals
This API is used to retrieve representation/data for specific merchant terminal.
The API can replay with one of the following HTTP status codes:
-
200 - request is valid and the terminal was retrieved successfully
-
401 - authentication credentials (JWT token) were missing or could not be validated
-
403 - authentication credentials do not carry required authorisation
-
404 - request is valid but failed to retrieve data because:
-
terminal was not found for the requested terminal number
-
terminal was found but no location was found for that terminal
-
location was found but no company was found for that location
-
-
-
-
409 - request is valid but multiple terminals were found for the requested terminal number
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 20x:
GET /terminals/{terminal_number} HTTP/1.1
Host: mygp.global
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
{
"terminal_number": "12345678",
"mid": "88587548578",
"business_id": "7587485784",
"terminal_type": "ICT220DTINTCL_ETH",
"receipt_rows": [
"receipt row #1",
"receipt row #2",
"receipt row #3
],
"activated": "2018-05-12",
"updated": "2020-09-27T10:16:12"
}
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 40x:
{
"code": "40x",
"message": "name of the error",
"description": "description details of the error",
}
Terminal List
This API is used to retrieve list of terminal for specific a location.
The API can replay with one of the following HTTP status codes:
-
200 - request is valid and the terminal list was retrieved successfully
-
401 - authentication credentials (JWT token) were missing or could not be validated
-
403 - authentication credentials do not carry required authorisation
-
404 - request is valid but the MID was not found
-
409 - request is valid but multiple MIDs were found for a specific location
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 20x:
GET /locations/{mid}/terminals HTTP/1.1
Host: mygp.global
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
{
"count": 2
"next": null,
"previous": null,
"results": [
{
"terminal_number" : "1234567891",
"terminal_type" : "ICT220DTINTCL_ETH",
"created" : "2019-07-01",
"modified" : "2019-07-01T01:00:00",
"self" : "https://mygp.global/v1/terminals/1234567891"
},
{
"terminal_number" : "1234567892",
"terminal_type" : "ICT220DTINTCL_ETH",
"created" : "2019-10-12",
"modified" : "2019-11-03T08:35:13",
"self" : "https://mygp.global/v1/terminals/1234567892"
}
]
}
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 40x:
{
"code": "40x",
"message": "name of the error",
"description": "description details of the error",
}
Subscription List
This API is used to retrieve list of subscriptions for a specific company.
The API can replay with one of the following HTTP status codes:
-
200 - request is valid and the location list was retrieved successfully
-
401 - authentication credentials (JWT token) were missing or could not be validated
-
403 - authentication credentials do not carry required authorisation
-
404 - request is valid but the business ID was not found
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 20x:
GET /companies/{business_id}/subscriptions HTTP/1.1
Host: mygp.global
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
{
"count": 2
"next": null,
"previous": null,
"results": [
{
"id" : "adcaac2d-26c0-4728-b2a9-4286bbd3e324",
"status" : "ACTIVE",
"created" : "2019-07-02T01:00:00.000Z",
"modified" : "2019-07-02T01:00:00.000Z",
"offer_id" : "6d5a1ef3-57fb-4739-abe7-fb1ecdac84af"
},
{
"id" : "fed2bd00-77f4-4346-a950-08d094c2a446",
"status" : "ACTIVE",
"created" : "2019-07-01T01:00:00.000Z",
"modified" : "2019-07-01T01:00:00.000Z",
"offer_id" : "645211e9-98db-48d7-a16c-768eb1d3db4a"
}
]
}
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 40x:
{
"code": "40x",
"message": "name of the error",
"description": "description details of the error",
}
Subscription management API
This chapter describes integration interfaces designed to facilitate integration of subscription lifecycle management between Global Payments Marketplace (GPM or marketplace) system and 3rd party system providing the service.
Lifecycle events originated from marketplace
Events discussed in this section originate in the GPM system and are submitted to the 3rd party systems in the form of HTTP requests (API calls).
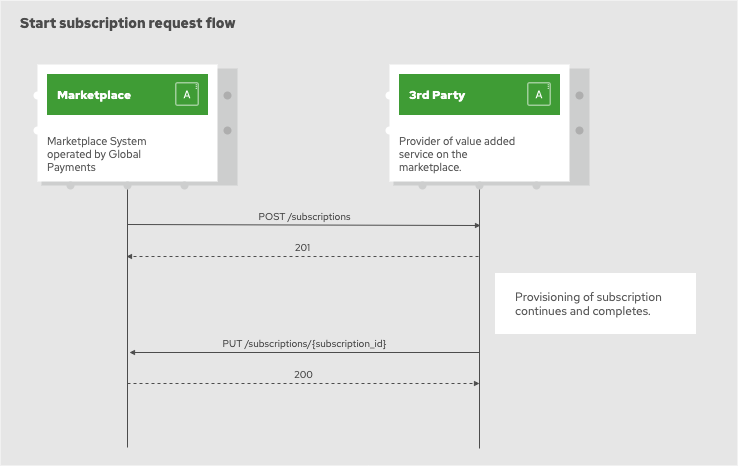
Start subscription
Request to start new subscription is submitted as a HTTP POST request to the /subscriptions endpoint on the
3rd party system.
Key parameters in the request body:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
market |
string |
Indicates customer market using a two-letter country code (ISO 3166-1 alpha-2) |
business_id |
string |
Contains the permanent company ID under which the company is doing business.E.g. Czech Republic and Slovakia the business_id corresponds to IČO. The length of the field varies between markets. |
company_key |
string |
Company key that can be used with different GPM APIs to identify particular company. The length of the field is 40 characters. |
offer_id |
string/uuid |
Contains pre-agreed UUID string identifying specific service offer that should be used for requested activation. Offer ID is provided in thr UUID format. It is created and assigned by the GPM system and shared with the partner. Example: 0001001-0003-0001-000000000001 |
capabilities |
list of strings |
Contains list of optional service capabilities that should be activated as part of the request. Capabilities are identified with pre-agreed identifiers shared between GPM and the partner. List may be empty if service does not support any optional capabilities or customer did not select any. |
outlets |
list of strings |
Contains list of outlet IDs that should be connected to the new service instance. This property can be empty if there were no outlets selected for subscription or even omitted if target service does not require this information. |
gateways |
list of strings |
Contains list of gateway IDs that should be connected to the new service instance. This property can be empty if there were no gateways selected for subscription or even omitted if target service does not require this information. |
Request body structure example:
POST /subscriptions HTTP/1.1
Host: www.3rd-party.com
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 328
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
RequestId: 1CAC7410-744B-44F2-B02E-5C15710D3F0D
{
"market":"CZ",
"business_id":"098765432112",
"customer_key":"23b1d7bcdb6fc513ba0edd8957943b6c30425948",
"offer_id":"3BE2B9E5-4C5C-4ED3-9F93-925DD77C0214",
"capabilities":[
"<CAPID01>",
"<CAPID02>"
],
"outlets":[
"<MID01>",
"<MID02>",
"<MID03>"
],
"gateways":[
"<MID11>",
"<MID12>",
"<MID13>"
]
}
3rd party system is expected to reply with one of the following HTTP status codes:
-
200 - new subscription was created and is ready for use
-
201 - request was accepted and subscription is in the process of being provisioned
-
400 - request did not pass validation on 3rd party system
-
401 - authentication credentials (JWT token) were missing or could not be validated
-
403 - authentication credentials do not carry required authorisation
-
422 - request is valid but cannot be accepted due to a conflict on the 3rd party system
-
5xx - technical problem on 3rd party system
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 20x:
RequestID: 1CAC7410-744B-44F2-B02E-5C15710D3F0D
{
'subscription_id': '{random subscription uuid}',
'attributes': {
'<name>': '<value>'
}
}
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 40x:
RequestID: 1CAC7410-744B-44F2-B02E-5C15710D3F0D
{
'reason': 'Short description of the reason.',
'details': {
'<name>': '<value>'
}
}
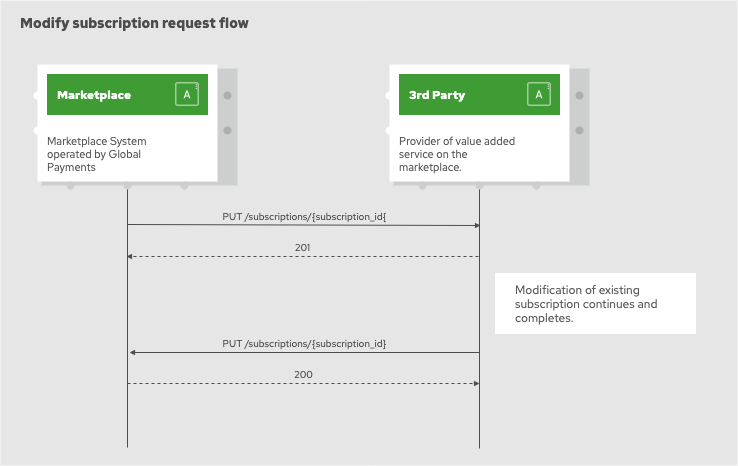
Update subscription
Request to modify existing subscription is submitted as a HTTP PUT request to the /subscriptions/{subscription_id}
endpoint on the 3rd party system.
Request body structure example:
PUT /subscriptions/{subscription_id} HTTP/1.1
Host: www.3rd-party.com
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 581
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
RequestId: 1CAC7410-744B-44F2-B02E-5C15710D3F0D
{
'offer_id': '3BE2B9E5-4C5C-4ED3-9F93-925DD77C0214',
'capabilities': [
'<CAPID01>',
'<CAPID02>',
'<CAPID03>'
],
'outlets': [
'<MID01>',
'<MID03>'
],
'gateways': [
'<MID11>',
'<MID12>'
]
}
3rd party system is expected to reply with one of the following HTTP status codes:
-
200 - subscription was found, updated and is ready for use
-
201 - request for modification was accepted and subscription is in the process of being updated
-
400 - request did not pass validation on 3rd party system
-
401 - authentication credentials (JWT token) were missing or could not be validated
-
403 - authentication credentials do not carry required authorisation
-
404 - target subscription record could not be located/retrieved by the 3rd party system
-
422 - request is valid but cannot be accepted due to a conflict on the 3rd party system
-
5xx - technical problem on 3rd party system
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 20x:
RequestID: 1CAC7410-744B-44F2-B02E-5C15710D3F0D
{
'subscription_id': '{subscription_id}',
'attributes': {
'<name>': '<value>'
}
}
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 40x:
RequestID: 1CAC7410-744B-44F2-B02E-5C15710D3F0D
{
'reason': 'Short description of the reason.',
'details': {
'<name>': '<value>'
}
}
The content of the request body passed with the update request must be interpreted by the server as the declaration of desired target state for the subscription. E.g. with the request body provided in the example the desired target state for the subscription is as follows:
-
capabilities CAPID01, CAPID02 and CAPID03 are enabled/applied
-
outlets MID01 and MID03 are covered by the subscription
-
gateways MID11 and MID12 are covered by the subscription
Cease subscription
Request to cease a subscription is submitted as a HTTP DELETE request to the /subscriptions/{subscription_id} endpoint
on the 3rd party system.
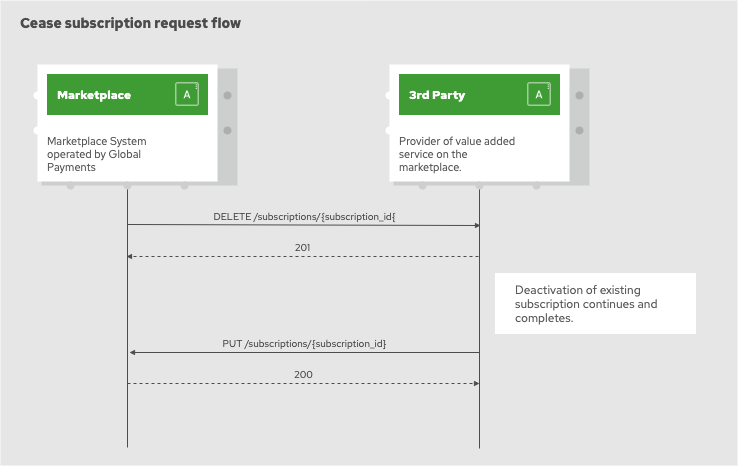
Request example:
DELETE /subscriptions/{subscription_id} HTTP/1.1
Host: www.3rd-party.com
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 581
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
RequestId: 1CAC7410-744B-44F2-B02E-5C15710D3F0D
3rd party system is expected to reply with one of the following HTTP status codes:
-
200 - subscription was found and ceased
-
201 - request to cease the subscription was accepted and subscription is in the process of being ceased
-
400 - request did not pass validation on 3rd party system
-
401 - authentication credentials (JWT token) were missing or could not be validated
-
403 - authentication credentials do not carry required authorisation
-
404 - target subscription record could not be located/retrieved by the 3rd party system
-
422 - request is valid but cannot be accepted due to a conflict on the 3rd party system
-
5xx - technical problem on 3rd party system
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 40x:
RequestID: 1CAC7410-744B-44F2-B02E-5C15710D3F0D
{
'reason': 'Short description of the reason.',
'details': {
'<name>': '<value>'
}
}
Lifecycle events originated from 3rd party
Events discussed in this section originate in the 3rd party system and are submitted to the Global Payments Marketplace the form of HTTP requests (API calls).
Subscription status update
Any changes to the subscription that originate in the 3rd party system and are significant from the customer relationship perspective must be reported to the marketplace. Such events include:
-
completion of subscription activation
-
completion of subscription modification
-
completion of subscription deactivation (cease)

Request to provide subscription status update is submitted as a HTTP PUT request to the /subscriptions/{subscription_id}
endpoint on the GPM system.
Request body structure example:
PUT /subscriptions/{subscription_id} HTTP/1.1
Host: api.mygp.global
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 581
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>
RequestId: 1CAC7410-744B-44F2-B02E-5C15710D3F0D
{
'status': 'ACTIVE',
'attributes': {
'<name>': '<value>'
}
}
GPM system is expected to reply with one of the following HTTP status codes:
-
200 - subscription status updated was accepted and processed
-
400 - request did not pass validation on GPM system
-
401 - authentication credentials (JWT token) were missing or could not be validated
-
403 - authentication credentials do not carry required authorisation
-
404 - target subscription record could not be located/retrieved by the GPM system
-
422 - request is valid but cannot be accepted due to a conflict on the GPM system
-
5xx - technical problem on GPM system
Response body structure for HTTP response codes 40x:
RequestID: 1CAC7410-744B-44F2-B02E-5C15710D3F0D
{
'reason': 'Short description of the reason.',
'details': {
'<name>': '<value>'
}
}
Subscription lifecycle states
Recognised states during the subscription lifecycle are:
| State | Description |
|---|---|
ACTIVATING |
Subscription activation process has been started. Normally this is the initial state after the GPM submitted request to partner system, which accepted the request and replied with HTTP status code 201, indicating that subscription activation is in progress. |
ACTIVE |
Subscription activation on the partner system has been completed successfully. This state is achieved if partner system replied with HTTP status code 200 upon initial request - meaning that activation request was completed synchronously - or when partner system submitted subscription status update request indicating that subscription is in active state. |
MODIFYING |
Subscription modification process has been started. Normally this state is entered after a modification request was submitted by the GPM to the partner system, which accepted the request and replied with HTTP status code 201, indicating that subscription modification is in progress. |
CEASING |
Subscription de-activation process has been started. Normally this state is entered after a deactivation request was submitted by the GPM to the partner system, which accepted the request and replied with HTTP status code 201, indicating that subscription deactivation is in progress. |
SUSPENDED |
Subscription has been suspended. Normally this is the intermediate state and is entered when partner system submitted subscription status update request indicating that subscription is in suspended state. |
CEASED |
Subscription has been deactivated. Normally this is the final state after the GPM submitted deactivation request to partner system, which accepted the request and replied with HTTP status code 200- meaning that deactivation request was completed synchronously - or when partner system submitted subscription status update request indicating that subscription is in ceased state. |
PAUSED |
Subscription has been paused by the customer. Customer cannot use the subscription while it is in the paused state, but subscription data is retained on the provider’s system and subscription can be resumed in the future. Support for this state is optional as it is not applicable for all services. |
Integration testing with sandbox APIs
Developers charged with implementation of integration between a service and GPM subscription lifecycle management APIs can use sandbox APIs provided by the GPM to help with the task. The purpose of the sandbox APIs is to allow developers to create test data (customer records, user accounts, etc) and trigger actions in GPM that will result in an integration event.
Complete specification of sandbox APIs can be viewed and downloaded from the main documentation page. This section is specifically dedicated to explain how sandbox APIs can be used for integration testing of subscription lifecycle management integration.
Prerequisite steps
|
Note
|
Examples of sandbox API usage provided in this section are using curl command line utility. A simplified CLI interface is being prepared and will be available in near future. |
Sandbox APIs are protected with OAuth-like authentication scheme, where every API request issued by the client must be supplied with a bearer token. Following recipes demonstrate how an access token can be obtained using a combination of command line utilities. These recipes depend on following command line utilities to be available on the system:
$ export KCCLIENT="test-client" $ export KCSECRET="ae85****-****-****-****-******60d9" $ export KCURL=https://uat1.mygp.cz/auth $ export KCREALM=mygp-cz $ export APIROOT=https://uat1-api.mygp.cz
$ export KCTOKEN=$(curl --silent \
--data "grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=${KCCLIENT}&client_secret=${KCSECRET}" \
${KCURL}/realms/${KCREALM}/protocol/openid-connect/token \
| jq -r .access_token)
$ echo $KCTOKEN eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCIgOiAiSldUIiwia2lkIiA6ICJ4b29DV...
Create new sandbox customer record
A customer record is required for most sandbox API operations and creation of new sandbox customer record is usually the first step in the flow of integration testing.
information
$ curl -s "${APIROOT}/v1/sandbox/customers" \
-X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer $KCTOKEN" \
| json_pp
{
"code":"200",
"message":"SUCCESS",
"description":"Sandbox customer record was created successfully.",
"customer_key":"658b426f3aa480d885edfeaa9e2d39b233a068bc",
"outlets":[
{
"locid":"MPLLOC000000000000047",
"location_number":"992020062739822"
}
],
"gateways":[
{
"locid":"MPLLOC000000000000048",
"location_number":"992020097484427"
}
]
}
The customer_key attribute reported in the response body is important and should be copied away somewhere safe and handy for reference with future requests.
$ curl -s "${APIROOT}/v1/sandbox/customers" \
-X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer $KCTOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "outlets": ["TESTMID000000000000001"], "gateways": ["TESTMID000000000000002"] }' \
| json_pp
{
"code":"200",
"message":"SUCCESS",
"description":"Sandbox customer record was created successfully.",
"customer_key":"658b426f3aa480d885edfeaa9e2d39b233a068bc",
"outlets":[
{
"locid":"TESTMID000000000000001",
"location_number":"992020062739822"
}
],
"gateways":[
{
"locid":"TESTMID000000000000002",
"location_number":"992020097484427"
}
]
}
This variant of sandbox customer record setup is useful when partner system depends on data that s related to specific well known MIDs (outlet and gateway IDs) and cannot work successfully with arbitrarily generated MIDs.
Create user account registration link for sandbox customer account
Customer records created through sandbox API are not automatically connected with a user account and require pairing. Paring is a process where customer record is linked with a new (or existing) user account. In order to start the pairing process, a (unique) account pairing invitation link must be generated through the onboarding API.
$ curl -s "${APIROOT}/v1/sandbox/users" \
-X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer $KCTOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "customer_key": "0b5dea3c19127741519c85dbcc53a547800cb84e" }' \
| json_pp
{
"code":"200",
"message":"SUCCESS",
"description":"Sandbox user account invitation was created successfully. Open invitation link in browser and complete user registration.",
"invitation_url":"https://uat1.mygp.cz/onboarding/QwZN0_clk4ItotzKS1UQCsIHsh8zugoy"
}
The URL link returned by the sandbox API can be used to pair new (or existing) user account with the sandbox customer record. Registration and pairing of user accounts is described in separate section of the document.
Modify outlet and gateway setup for sandbox customer record
$ curl -s "${APIROOT}/v1/sandbox/customers/aadc655afa2f75ccc93edb88dbc923c1aeea83d5/add-outlets" \
-X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $KCTOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "outlets": ["TESTMID000000000000003"] }' \
| json_pp
{
"code":"200",
"message":"SUCCESS",
"description":"Sandbox customer record was updated successfully with new outlets.",
"outlets":[
{
"locid":"TESTMID000000000000003",
"location_number":"992020018847857"
}
]
}
|
Important
|
As in the previous request to create sandbox customer record the MIDs (outlet/gateway IDs) must be unique and unknown on the system. |
$ curl -s "${APIROOT}/v1/sandbox/customers/aadc655afa2f75ccc93edb88dbc923c1aeea83d5/remove-outlets" \
-X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $KCTOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "outlets": ["TESTMID000000000000001"] }' \
| json_pp
{
"code":"200",
"message":"SUCCESS",
"description":"Sandbox customer record was updated successfully."
}
$ curl -s "${APIROOT}/v1/sandbox/customers/aadc655afa2f75ccc93edb88dbc923c1aeea83d5/add-gateways" \
-X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $KCTOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "gateways": ["TESTMID000000000000004", "TESTMID000000000000005"] }' \
| json_pp
{
"code":"200",
"message":"SUCCESS",
"description":"Sandbox customer record was updated successfully with new gateways.",
"outlets":[
{
"locid":"TESTMID000000000000004",
"location_number":"992020018847858"
},
{
"locid":"TESTMID000000000000005",
"location_number":"992020018847859"
}
]
}
$ curl -s "${APIROOT}/v1/sandbox/customers/aadc655afa2f75ccc93edb88dbc923c1aeea83d5/remove-gateways" \
-X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $KCTOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "gateways": ["TESTMID000000000000002"] }' \
| json_pp
{
"code":"200",
"message":"SUCCESS",
"description":"Sandbox customer record was updated successfully."
}
Initiate start subscription transaction on GPM
Start subscription transaction is triggered by creating a sandbox order where:
-
customer_key property of the request body JSON object is set to a value previously returned from create sandbox customer request,
-
offer_id property of the request body JSON object is set to a value defined in the partner catalog,
-
operation is set to ADD.
$ curl -s "${APIROOT}/v1/sandbox/orders" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $KCTOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "customer_key": "aadc655afa2f75ccc93edb88dbc923c1aeea83d5", "offer_id": "18CB9C1F-6CA8-4C67-8401-E104485FED3D", "operation": "ADD" }' \
| json_pp
{
"code":"200",
"message":"SUCCESS",
"description":"Sandbox customer order was created successfully.",
"order_id":"50736515-72e5-44b3-a252-518dbbf4d005"
}
When customer order was created successfully, GPM should respond within short time-frame (max 60 seconds) by invoking the registered start subscription endpoint of the partner system.
Initiate update subscription transaction on GPM
Update subscription transaction is triggered by creating a sandbox order where:
-
customer_key property of the request body JSON object is set to a value previously returned from create sandbox customer request,
-
offer_id property of the request body JSON object is set to a value defined in the partner catalog,
-
operation is set to MODIFY,
-
subscription_id property of the request body JSON object is set to a value generated for the previously created subscription by the partner system.
$ curl -s \
"${APIROOT}/v1/sandbox/orders" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $KCTOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "customer_key": "aadc655afa2f75ccc93edb88dbc923c1aeea83d5", "offer_id": "18CB9C1F-6CA8-4C67-8401-E104485FED3D", "operation": "MODIFY", "subscription_id": "6d1444f8-926b-4b72-94a6-374468370d74" }' \
| json_pp
{
"code":"200",
"message":"SUCCESS",
"description":"Sandbox customer order was created successfully.",
"order_id":"edf0ee7a-abd7-46d6-8959-9a9a8a792e6c"
}
When customer order was created successfully, GPM should respond within short time-frame (max 60 seconds) by invoking the registered update subscription endpoint of the partner system.
Initiate cease subscription transaction on GPM
Cease subscription transaction is triggered by creating a sandbox order where:
-
customer_key property of the request body JSON object is set to a value previously returned from create sandbox customer request,
-
offer_id property of the request body JSON object is set to a value defined in the partner catalog,
-
operation is set to REMOVE,
-
subscription_id property of the request body JSON object is set to a value generated for the previously created subscription by the partner system.
$ curl -s "${APIROOT}/v1/sandbox/orders" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $KCTOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "customer_key": "aadc655afa2f75ccc93edb88dbc923c1aeea83d5", "offer_id": "18CB9C1F-6CA8-4C67-8401-E104485FED3D", "operation": "REMOVE", "subscription_id": "6d1444f8-926b-4b72-94a6-374468370d74" }' \
| json_pp
{
"code":"200",
"message":"SUCCESS",
"description":"Sandbox customer order was created successfully.",
"order_id":"cdbdd558-711a-48bd-910b-4c6cde28aa70"
}
When customer order was created successfully, GPM should respond within short time-frame (max 60 seconds) by invoking the registered cease subscription endpoint of the partner system.
Retrieve subscription information for sandbox customer on GPM
An auxiliary HTTP GET operation is exposed in the sandbox API that can be used to retrieve information about active subscriptions for the sandbox customer record. Only subscriptions that are managed by the user account supplied with authentication credentials are returned.
$ curl --s \
"${APIROOT}/v1/sandbox/customers/4c4c57b98ddaf30d8b5aa96c311d92a7d3098eb9/subscriptions" \
-X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $KCTOKEN" \
| json_pp
{
"code":"200",
"message":"SUCCESS",
"description":"Sandbox customer subscriptions were retrieved successfully.",
"count":1,
"items":[
{
"subscription_id":"93518b0c-a297-4862-9b45-6e579f20f793",
"offer_id":"6ac389b4-09e6-43c8-be74-c4fb1c23a792",
"status":"ACTIVE",
"origin_id":"48e87148-b3df-4f5a-ba66-8bfa0813efde",
"created":"2020-04-27T21:33:20.566451Z",
"modified":"2020-04-27T21:39:01.523046Z"
}
]
}
Revision history
| Revision | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|
8 |
27.4.2020 |
Updated sandbox API documentation with example for get sandbox customer subscriptions request. |
7 |
15.4.2020 |
Updated sandbox API examples with recent extensions to response objects for some operations. |
6 |
31.3.2020 |
Updated sandbox API examples with added line breaks for readability. References to company_key in API docs and examples replaced with customer key where appropriate. |
5 |
18.3.2020 |
Added section about using sandbox API as a test utility for integration of subscription lifecycle management. |
4 |
20.2.2020 |
List of supported locale codes added to the document. |
3 |
15.2.2020 |
Expended section on JWT validation. Clarified requirements for API request authentication. |
2 |
11.2.2020 |
Content related to API integration (e.g. authentication) moved to its own chapter. Added description for JWT token validation. Added document preamble with introduction of markets and endpoint locations. |
1 |
30.1.2020 |
Separate documents consolidated into single one. |